MemoryStream和BufferedStream都派生自基类Stream,因此它们有很多共同的属性和方法,但是每一个类都有自己独特的用法。这两个类都是实现对内存进行数据读写的功能,而不是对持久性存储器进行读写。
读写内存-MemoryStream类
MemoryStream类用于向内存而不是磁盘读写数据。MemoryStream封装以无符号字节数组形式存储的数据,该数组在创建MemoryStream对象时被初始化,或者该数组可创建为空数组。可在内存中直接访问这些封装的数据。内存流可降低应用程序中对临时缓冲区和临时文件的需要。
下表列出了MemoryStream类的重要方法:
1、Read():读取MemoryStream流对象,将值写入缓存区。
2、ReadByte():从MemoryStream流中读取一个字节。
3、Write():将值从缓存区写入MemoryStream流对象。
4、WriteByte():从缓存区写入MemoytStream流对象一个字节。
Read方法使用的语法如下:
mmstream.Read(byte[] buffer,offset,count)
其中mmstream为MemoryStream类的一个流对象,3个参数中,buffer包含指定的字节数组,该数组中,从offset到(offset +count-1)之间的值由当前流中读取的字符替换。Offset是指Buffer中的字节偏移量,从此处开始读取。Count是指最多读取的字节数。Write()方法和Read()方法具有相同的参数类型。
MemoryStream类的使用实例:
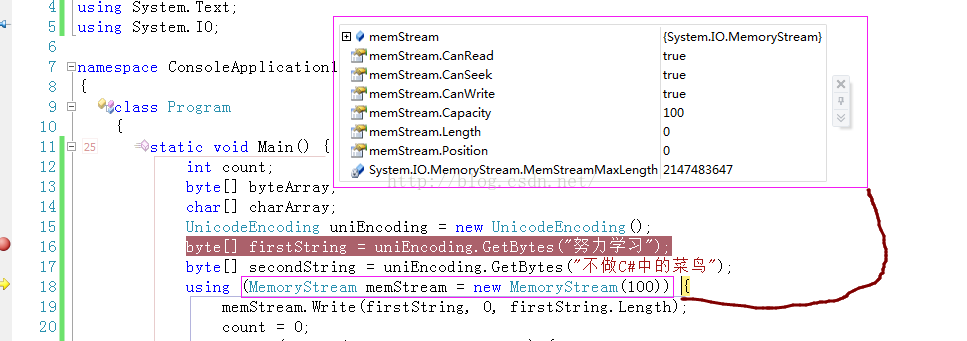
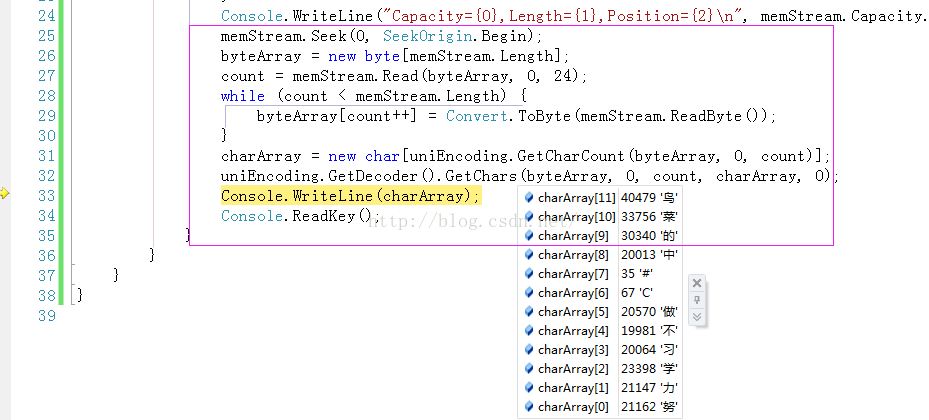
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Text;using System.IO; namespace ConsoleApplication1{ class Program { static void Main() { int count; byte[] byteArray; char[] charArray; UnicodeEncoding uniEncoding = new UnicodeEncoding(); // Create the data to write to the stream. byte[] firstString = uniEncoding.GetBytes("一二三四五"); byte[] secondString = uniEncoding.GetBytes("上山打老虎"); using (MemoryStream memStream = new MemoryStream(100)) { // Write the first string to the stream. memStream.Write(firstString, 0, firstString.Length); // Write the second string to the stream, byte by byte. count = 0; while (count < secondString.Length) { memStream.WriteByte(secondString[count++]); } // Write the stream properties to the console. Console.WriteLine("Capacity={0},Length={1},Position={2}\n", memStream.Capacity.ToString(), memStream.Length.ToString(), memStream.Position.ToString()); // Set the position to the beginning of the stream. memStream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin); // Read the first 20 bytes from the stream. byteArray = new byte[memStream.Length]; count = memStream.Read(byteArray, 0, 20); // Read the remaining bytes, byte by byte. while (count < memStream.Length) { byteArray[count++] = Convert.ToByte(memStream.ReadByte()); } // Decode the byte array into a char array // and write it to the console. charArray = new char[uniEncoding.GetCharCount(byteArray, 0, count)]; uniEncoding.GetDecoder().GetChars(byteArray, 0, count, charArray, 0); Console.WriteLine(charArray); Console.ReadKey(); } } }} 在这个实例代码中使用了using关键字。注意:
using 关键字有两个主要用途:
1、作为指令,用于为命名空间创建别名或导入其他命名空间中定义的类型。
例如:
using System;
2、作为语句,用于定义一个范围,在此范围的末尾将释放对象。
using(Connection conn=new Connection(connStr)) { } //使用using关键字可及时销毁对象
MemoryStream.Capacity 属性 取得或设定配置给这个资料流的位元组数目。
MemoryStream.Position 属性 指定当前流的位置。
MemoryStream.Length 属性获取用字节表示的流长度。
SeekOrigin()是一个枚举类,作用设定流的一个参数。
SeekOrigin.Begin我得理解就是文件的最开始,“0”是偏移,表示跳过0个字节。写2就是跳过2个字节。
MemoryStream类通过字节读写数据。本例中定义了写入的字节数组,为了更好的说明Write和WriteByte的异同,在代码中声明了两个byte数组,其中一个数组写入时调用Write方法,通过指定该方法的三个参数实现如何写入。
另一个数组调用了WriteByte方法,每次写入一个字节,所以采用while循环来完成全部字节的写入。写入MemoryStream后,可以检索该流的容量,实际长度,当前流的位置,将这些值输出到控制台。通过观察结果,可以确定写入MemoryStream流是否成功。
调用Read和ReadByte两种方法读取MemoryStream流中的数据,并将其进行Unicode编码后输出到控制台。

读取内存流中的数据
在.NET中,使用抽象基类System.IO.Stream代表流,它提供Read和Write两个方法。由于数据流的有序性,因此流对象还有一个读写指针,为此,Stream类还有一个Seek方法用于移动读写指针。
字符串与字节数组间的互相转化:
string str = "内存大小"; byte[] temp = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes (str); // 字符串转化为字节数组 string s = Encoding.UTF8.GetString (temp); // 字节数组转化为字符串 Debug.Log (s);
Encoding用法比较简单,如果只是字节和字符的互相转换,GetBytes()和GetChars()这两个方法及它们的重载基本上会满足你所有要求。
GetByteCount()及其重载是得到一个字符串转换成字节时实际的字节个数。
GetCharCount()及其重载是得到一个字节数组转换成字符串的大小。
Decoder.GetChars 方法
Java里一个byte取值范围是-128~127, 而C#里一个byte是0~255.
首位不同. 但是底层I/O存储的数据是一样的
FileStream对象的数据来自文件,而MemoryStream对象的数据来自内存缓冲区。这两个类都继承自Stream类。
MemoryStream的数据来自内存中的一块连续区域,这块区域称为“缓冲区(Buffer)”。可以把缓冲区看成一个数组,每个数组元素可以存放一个字节的数据。
在创建MemoryStream对象时,可以指定缓冲区的大小,并且可以在需要的时候更改。 //字节数组 byte[] buffer = new byte[600]; //填充字节数组 private void CreateExampleData() { for(int i=0; i<600; i++) { //byte类型的数最大不能超过255,用256取模实现 buffer[i] = (byte)(i%256); } }内存流的基本使用方法: private void OnTestMemory() { //创建测试数据 CreateExampleData(); //创建内存流对象,初始分配50字节的缓冲区 MemoryStream mem = new MemoryStream(50); //向内存流中写入字节数组的所有数据 mem.Write(buffer,0,buffer.GetLength(0)); MessageBox.Show("写入数据后的内存流长度:" + mem.Length.ToString()); MessageBox.Show("分配给内存流的缓冲区大小:" + mem.Capacity.ToString()); mem.SetLength(550); MessageBox.Show("调用SetLength方法后的内存流长度:" + mem.Length.ToString()); mem.Capacity = 620;//此值不能小于Length属性 MessageBox.Show("调用Capacity方法后缓冲区大小:" + mem.Capacity.ToString()); //将读写指针移到距流开头10个字节的位置 mem.Seek(10,SeekOrigin.Begin); MessageBox.Show(mem.ReadByte().ToString()); mem.Close(); }内存流的Length属性代表了其中存放的数据的真实长度,而Capacity属性则代表了分配给内存流的内存空间大小。可以使用字节数组创建一个固定大小的MemoryStream, MemoryStream mem = new MemoryStream(buffer);这时,无法再设置Capacity属性的大小。还可以创建只读的内存流对象。 MemoryStream mem = new MemoryStream(buffer,false); FlieStream用于存取文件。创建文件并写入内容: //创建一个新文件 FileStream fsForWrite = new FileStream("test.data",FileMode.Create); try { //写入一个字节 fsForWrite.WriteByte(100); CreateExampleData(); //将字节数组写入文件 fsForWrite.Write(buffer,0,buffer.GetLength(0)); } catch(Exception ex) { MessageBox.Show(ex.Message); } finally { //关闭文件 fsForWrite.Close(); }打开文件并读取内容: private void ReadFromFile() { FileStream fsForRead = new FileStream("test.data",FileMode.Open); try { //读入一个字节 MessageBox.Show("文件的第一个字节为:"+fsForRead.ReadByte().ToString()); //读写指针移到距开头10个字节处 fsForRead.Seek(10,SeekOrigin.Begin); byte[] bs = new byte[10]; //从文件中读取10个字节放到数组bs中 fsForRead.Read(bs,0,10); } catch(Exception ex) { MessageBox.Show(ex.Message); } finally { fsForRead.Close(); } }如果一个程序退出了,但它打开的文件没有被关闭,将导致其他程序无法修改或删除此文件。 FileStream与MemoryStream间的相互作用:
-----解决方案--------------------
FileStream fs = new FileStream(path, FileMode.Open); byte[] data = new byte[fs.Length]; fs.Read(data, 0, data.Length); fs.Close(); MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream(data);
------解决方案--------------------
///定义并实例化一个内存流,以存放图片的字节数组。 MemoryStream m = new MemoryStream(); ///获得当前路径 string strAppPath = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory; //获得可执行文件的路径。 ///获得图片路径 string strPath = strAppPath + "img\\default.jpg"; ///图片读入FileStream FileStream f = new FileStream(strPath, FileMode.open); ///把FileStream写入MemoryStream m.SetLength(f.Length); f.Read(m.GetBuffer(), 0, (int)f.Length); m.Flush(); f.Close();
------解决方案--------------------
FileStream fs = new FileStream(fileName, FileMode.Open); byte[] MyData = new byte[fs.Length]; fs.Read(MyData, 0, (int)fs.Length); fs.Close(); MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream(MyData);
------解决方案--------------------
MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream(File.ReadAllBytes("c:\\1.jpg")); 原文:https://blog.csdn.net/e295166319/article/details/52702461